Transformers in Electronics and Power Distribution
An electrical transformer, often simply called a transformer, is a passive electrical component that plays a crucial role in power systems and electronics. This type of transformer transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through electromagnetic induction. Transformers in electrical systems are key components in power supplies, audio equipment, and communication systems.
What is a Transformer?
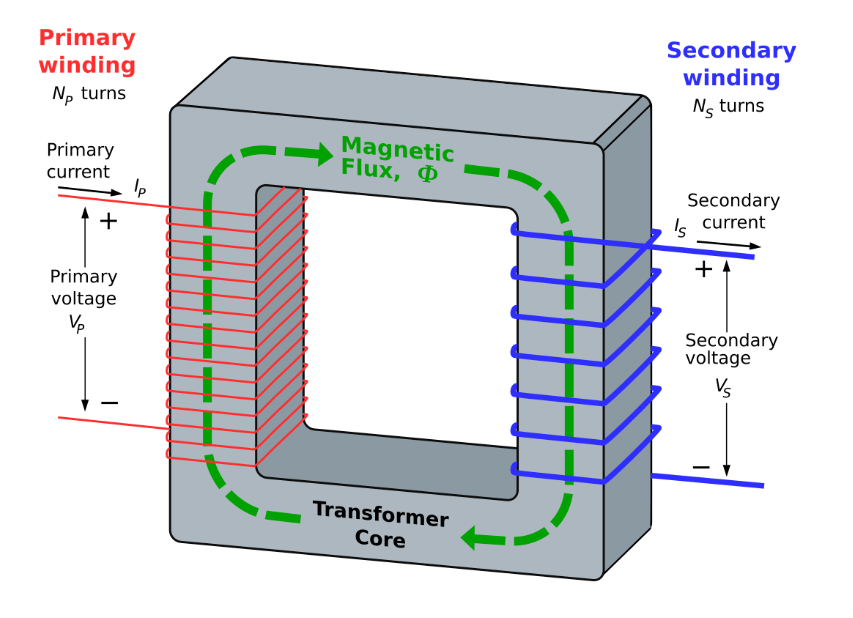
A transformer operates on the principle of mutual inductance, which is based on Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. It consists of at least two coils of wire wrapped around a core, often made of iron. These coils are not electrically connected but are magnetically linked through the core. When an alternating current (AC) flows through the first coil (primary winding), it creates a changing magnetic field. This field passes through the core and links with the second coil (secondary winding), inducing a voltage in it. The induced voltage can be higher or lower than the primary coil's voltage, depending on the number of turns in each coil. This principle forms the basis of transformer action and is crucial for understanding transformer energy transfer and transformer voltage transformation.
The Basic Parts of a Transformer
A typical transformer has three main components:
Primary winding: The first coil of wire connected to the AC power source.
Secondary winding: The second coil of wire connected to the load or device that will use the power.
Core: The material that links the two coils and directs the magnetic flux from the primary winding to the secondary winding. Iron cores are common due to their excellent magnetic properties. The transformer core is a critical component in determining the efficiency and performance of the transformer. Different core materials, such as silicon steel or ferrite, can be used depending on the application. For instance, an iron core transformer is commonly used in power applications, while a ferrite core transformer might be preferred in high-frequency applications. An air core transformer is another type used in specific high-frequency applications where magnetic core losses need to be minimized.
How a Transformer Works
Transformer basics revolve around the interaction between electrical currents and magnetic fields. A transformer works exclusively with AC power and does not function with direct current (DC). When AC flows through the primary winding, it generates a changing magnetic field. This field fluctuates in strength and direction with the AC signal, cutting through the secondary winding and inducing an AC voltage in it. This principle is fundamental to the operation of AC transformers.
The relationship between the voltages in the primary and secondary windings is determined by the transformer turns ratio. This ratio is equal to the number of turns in each coil and determines the voltage ratio. If the secondary winding has more turns than the primary winding, the output voltage is higher, creating a step-up transformer. Conversely, if the secondary winding has fewer turns, the output voltage is lower, resulting in a step-down transformer.
In an ideal transformer, the power in the primary circuit is nearly identical to the power in the secondary circuit. This principle is crucial for understanding transformer efficiency and voltage transformation. As power is the product of voltage and current, an increase in voltage leads to a proportional decrease in current, and vice versa. This relationship is governed by transformer equations, which are fundamental to analyzing transformer circuits and predicting their behavior.
Types of Transformers
Different transformer types vary widely based on their design and application. Here are some common types:
Step-up transformer: Raises voltage, often used in power plants to increase voltage for long-distance power transmission.
Step-down transformer: Reduces voltage, commonly used in homes and offices to lower high power line voltage to a safe level for electronics. This type of transformer is essential for stepping down voltage in distribution systems.
Isolation transformer: Has an equal number of turns in both windings, maintaining the same input and output voltages while providing electrical isolation between circuits. This type offers galvanic isolation, which is crucial in many applications for safety and noise reduction.
Autotransformer: Contains only one coil, with portions of the coil serving as both primary and secondary windings. It's more compact and cost-effective but doesn't offer circuit isolation.
Audio transformer: Used in audio circuits to match impedances between different components, ensuring maximum power transfer.
Other types of transformer include current transformers, voltage transformers, instrument transformers, and distribution transformers, each designed for specific applications in power systems and electronics. Some specialized types include the dry type transformer, single phase transformer, three-phase transformer, and shell type transformer. Additionally, there are resonant transformers for generating high voltages at high frequencies, and amorphous metal transformers known for their high efficiency. The toroidal transformer is known for its compact size and low electromagnetic interference, while the grounding transformer is used to provide a ground reference in ungrounded power systems. A variable differential transformer is a specialized type used for precise measurements in industrial applications.
Common Uses of Transformers
Transformer applications are diverse and ubiquitous in our daily lives:
Power Supplies
A transformer is a key component in almost every power supply. It steps down the high voltage AC from wall outlets to a lower, safer voltage. This is then rectified and filtered to produce the DC power required by most electronic devices. You'll find these power supplies in chargers for phones, laptops, and various other gadgets. The transformer circuit in these power supplies is crucial for converting high voltage AC to usable low voltage DC. A rectifier transformer is specifically designed for this AC to DC conversion process.
Power Transmission
Power transformers play a vital role in electrical grids. Power plants generate electricity at relatively low voltages, which is then stepped up by transformers for long-distance transmission. This high-voltage power travels efficiently through power lines, minimizing energy loss. At substations near urban areas, step-down transformers lower the voltage before it's distributed to homes and businesses. This process of stepping down voltage is essential for safe and efficient power distribution. Substation transformers and distribution transformers are critical components in this power delivery chain. Some systems also employ reverse feeding or back feeding techniques, where power can flow in the opposite direction, such as in systems with distributed energy generation.
Audio and Communication
In audio equipment, transformers are used for impedance matching, particularly in speaker systems. This ensures optimal performance between amplifiers and speakers. In communication systems, transformers provide electrical isolation and signal level matching, commonly seen in telephone lines and modems. The frequency response of these transformers is crucial for maintaining signal quality. Pulse transformers are used in digital communication systems for transmitting high-speed electrical pulses with minimal distortion.
How Transformers Relate to RAM and Computer Systems
While transformers don't directly interact with computer components like RAM or CPUs, they are crucial in providing stable power to these systems. Every computer relies on a Power Supply Unit (PSU) that converts high-voltage AC from the wall outlet into low-voltage DC required by the motherboard and its components.
The main transformer in the PSU is the first stage of this conversion process. It steps down the voltage before other components clean and stabilize the signal. This stable power supply is vital for all computer parts, including the CPU, graphics card, and RAM modules. Whether a computer has 8 GB RAM or 16 GB RAM, a consistent and clean power source is essential for reliable operation.
How a Transformer Is Made
The construction of a transformer involves several key steps:
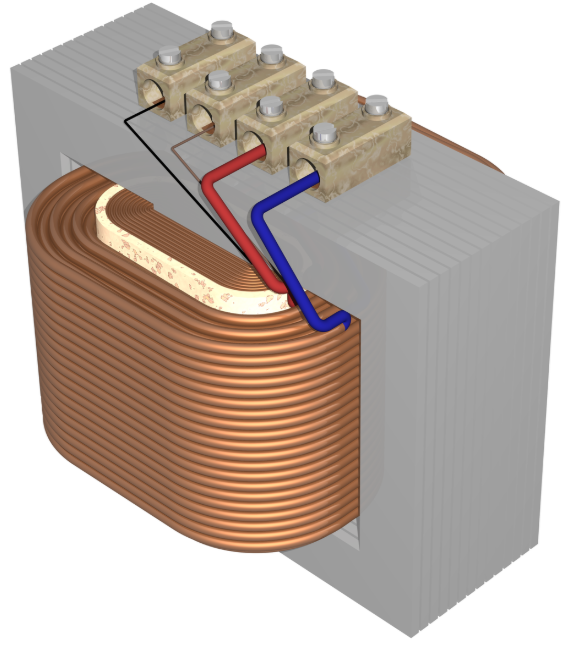
Transformer windings: Copper wire is precisely wrapped around a core. The number of turns determines the output voltage.
Insulation: The wire is coated with enamel to prevent short circuits between turns.
Core construction: The core is made of thin sheets of iron called laminations, stacked together to reduce energy loss from eddy currents. The laminated core design is crucial for minimizing transformer losses.
Some transformers, especially larger ones used in power distribution, use transformer oil for insulation and cooling. This oil helps dissipate heat and prevents arcing between components. These are known as oil type transformers and are commonly used in high-power applications. High voltage bushings are used to insulate and support the conductors where they exit the transformer tank. These bushings are critical components in maintaining the integrity and safety of the transformer system.
Transformer Efficiency and Losses
Transformer efficiency is a crucial consideration in their design and application. While transformers are generally highly efficient devices, they do experience some losses:
Core losses: These include hysteresis losses and eddy current losses in the transformer's core. The flux density in the core is a key factor in determining these losses.
Copper losses: Also known as I²R losses, these occur due to the resistance of the copper windings.
Flux leakage: Some magnetic flux doesn't link both windings, reducing efficiency. This is related to leakage inductance, which affects the transformer's performance.
Engineers work to minimize these transformer losses through careful design, choice of materials, and construction techniques. The efficiency of a transformer is often expressed as a percentage and is an important factor in its overall performance. Load losses occur when the transformer is under load, while no-load losses are present even when the transformer is energized but not supplying power to a load. The magnetizing current, which is present even when the transformer is unloaded, contributes to these no-load losses.
Advanced transformer designs may incorporate features like tap changers, which allow for adjustment of the turns ratio to optimize performance under varying load conditions. The delta-wye connection is another important concept in three-phase transformers, offering different advantages in terms of voltage regulation and harmonic suppression.
Conclusion
Transformers are simple yet powerful devices that change AC voltage levels using the principle of electromagnetic induction. They are fundamental to our electrical infrastructure, found in power grids, power supplies, and countless electronic devices. From step-up transformers in power plants to step-down transformers in our homes, these devices ensure that the right voltage reaches every electrical and electronic device.
The versatility of transformers extends from the massive units in electrical substations to the tiny components in our everyday gadgets. Their role in providing stable, appropriate power is essential for all electronics, from simple circuits to complex computer systems with substantial RAM. As we continue to rely more heavily on electronic devices and power systems, the importance of transformers in our technological landscape only grows.
Understanding transformer basics and how transformers work is crucial for anyone interested in electrical engineering, power systems, or electronics. These devices exemplify the practical application of electromagnetic principles, demonstrating how simple physical laws can be harnessed to create powerful and efficient energy transfer systems. From the basic transformer circuit to complex power transformer types, the principles of transformer action remain consistent, making them a cornerstone of modern electrical systems.
The design of transformers involves considerations such as vector group (which describes the phase relationship between primary and secondary windings), delta-wye connections, power rating, and kVA rating. Advanced concepts like voltage regulation, inrush current, and the use of tap changers for adjusting voltage ratios are also important in transformer design and operation.
As technology advances, new types of transformers continue to emerge, such as toroidal transformers, known for their compact size and low electromagnetic interference, and grounding transformers, used to provide a ground reference in ungrounded power systems. Specialized transformers like rectifier transformers for AC to DC conversion and pulse transformers for generating or transmitting high-speed electrical pulses showcase the ongoing evolution and diversification of transformer technology.