What Is a Decoder Chip? Types, Applications & Buying Guide
Electronics devices—from industrial control panels to consumer audio gear and automotive ADAS systems—rely on a critical component to translate encoded signals into usable data: the decoder chip. Simply put, a decoder chip acts as the "signal translator" of electronic systems, converting complex encoded signals (digital or analog) into clear, actionable information that devices can process.
This guide covers the core basics of decoder chips, breaks down their key types and real-world applications, and shares essential buying tips for electronics procurement professionals. For buyers, choosing the right decoder chip starts with matching specs to your use case—and partnering with a supplier that offers authentic products, massive inventory, and reliable delivery. Joydo, a leading chip procurement specialist, stocks a wide range of decoder chips from top brands, ensuring you get the right components when you need them.
What Is a Decoder Chip?
A decoder chip is an integrated circuit (IC) designed to convert encoded input signals (such as binary, BCD, or digital audio signals) into a decoded output format that electronic devices can directly use. Unlike a general "decoder" (which may refer to a standalone device), a decoder chip is a miniaturized, integrated component—small in size, low in power consumption, and suitable for embedding in various compact electronic products.
Its core working principle is straightforward: it receives a specific encoded signal (the "input"), processes it through internal logic circuits, and outputs a clear signal (the "output") that drives other components. For example, in a car's ADAS system, a decoder chip parses the encoded data from the radar sensor into distance and speed information, which is then sent to the vehicle's control unit to trigger safety functions like automatic braking.
It’s important to distinguish decoder chips from encoder chips: encoder chips convert analog signals to digital signals (the "encoding" process), while decoder chips reverse this process (the "decoding" process). Together, they form a complete signal conversion chain in many electronic systems.
Key Types of Decoder Chips & Their Applications
Decoder chips are classified by their signal conversion functions and application scenarios. Below are the most common types, along with their core uses and procurement considerations—with insights into Joydo's inventory advantages for each category.
BCD Decoder Chips
BCD (Binary-Coded Decimal) decoder chips convert 4-bit binary encoded signals into decimal digits (0-9) and corresponding control signals. They are widely used in scenarios that require digital display, such as industrial control panels, digital counters, electronic scales, and household appliance control interfaces.
Procurement Notes: Focus on voltage compatibility (most industrial-grade models support 5.5V-18V) and output drive capability. Joydo stocks BCD decoder chips from top brands like Texas Instruments (e.g., SN74LS47) and Onsemi, with bulk inventory available for immediate delivery—ideal for industrial manufacturers with large-volume orders.
Audio Decoder Chips
Audio decoder chips specialize in converting digital audio signals (e.g., MP3, AAC, FLAC) into analog audio signals that can drive speakers or headphones. They are the core components of audio devices such as Bluetooth speakers, wireless headphones, car infotainment systems, and home theaters.
Procurement Notes: Prioritize parameters like signal-to-noise ratio (SNR, preferably ≥90dB) and power consumption (critical for portable devices). Joydo’s audio decoder chip inventory includes high-performance models from Cirrus Logic (e.g., CS4398) and AKM, covering both consumer and automotive-grade requirements.
Address Decoder Chips
Address decoder chips are used in computer motherboards, microcontroller systems, and industrial control boards. Their main function is to decode the address signal sent by the CPU or microcontroller, identifying which memory unit or peripheral device needs to be accessed—ensuring accurate data transmission in complex electronic systems.
Procurement Notes: Compatibility with the system’s bus width (8-bit/16-bit/32-bit) is key. Joydo offers address decoder chips from Toshiba and STMicroelectronics, with models supporting a wide range of bus standards and immediate stock availability to avoid production delays.
Video Decoder Chips
Video decoder chips convert compressed digital video signals (e.g., H.264, H.265) into uncompressed video frames for display. They are used in security cameras, smart TVs, set-top boxes, and video surveillance systems.
Procurement Notes: Focus on supported video formats and resolution (e.g., 4K/8K compatibility). Joydo stocks video decoder chips from Ambarella and Hisilicon, suitable for both consumer and professional surveillance applications.
Decoder Chip Buying Guide for Electronics Buyers
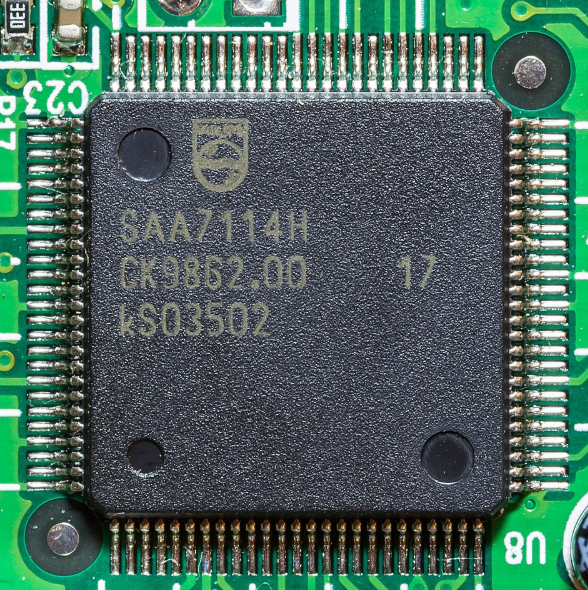

Procuring decoder chips requires balancing technical compatibility, quality reliability, and supply stability. Below are 4 actionable tips to help you make informed decisions—with insights into how Joydo addresses common procurement pain points.
Match the Chip Type to Your Application Scenario
Different scenarios have unique requirements:
Industrial control: Choose industrial-grade decoder chips (e.g., BCD, address decoders) with wide temperature resistance (-40℃ to +125℃) and anti-interference capabilities.
Consumer electronics (audio/ video): Prioritize low-power, high-performance models (e.g., audio decoders with high SNR, video decoders with 4K support).
Automotive applications: Select automotive-grade decoder chips (AEC-Q100 certified) that can withstand high temperatures and vibration.
Verify Key Technical Parameters
Ensure the decoder chip’s specs match your system:
Voltage range: Confirm compatibility with your device’s power supply (e.g., 3.3V for consumer electronics, 12V for industrial systems).
Package type: Choose packages suitable for your PCB design (e.g., SOIC for compact devices, PDIP for easy soldering in prototyping).
Signal format: For audio/video decoders, confirm support for your target signal formats (e.g., H.265 for video, MP3/AAC for audio).
Prioritize Authentic, Brand-Authorized Products
Counterfeit decoder chips can cause device malfunctions, safety risks, and production delays. Always choose suppliers that provide brand-authorized products with quality certificates. Joydo sources all decoder chips directly from official brand distributors (TI, Cirrus Logic, Toshiba, etc.), with full traceability and quality assurance.
Choose Suppliers with Stable Inventory & Fast Delivery
Stockouts are a major risk in chip procurement. Partner with suppliers that have massive inventory and flexible delivery options. Joydo maintains a large stock of decoder chips, covering mainstream types and models—supporting bulk orders, small-batch purchases, and urgent delivery to meet your production schedule.
Conclusion
Decoder chips are the unsung heroes of modern electronics, enabling signal conversion across industrial, consumer, and automotive sectors. Understanding their types, applications, and procurement key points is critical for ensuring device performance and production efficiency.
For electronics procurement professionals, the key to successful decoder chip procurement lies in two core steps: 1) Matching the right chip type and parameters to your application scenario; 2) Partnering with a reliable supplier that offers authentic products, massive inventory, and fast delivery.
Joydo specializes in chip procurement, with a wide range of authentic decoder chips from top global brands (TI, Cirrus Logic, Toshiba, etc.) in stock. Whether you need bulk orders for industrial production or small-batch purchases for prototyping, we provide tailored solutions to meet your needs. Contact Joydo today for your decoder chip procurement requirements.