AI Chips vs GPU: Key Differences and Applications
AI chips are special computer parts. They are made to handle hard calculations for AI tasks. These tasks need many operations at the same time. AI chips can do this work faster than normal computer parts. They can also use less power while doing heavy calculations. AI chips are designed to make machines learn and think in ways like humans.
GPUs are also strong computer parts. They are used first for graphics. GPUs can handle many tasks at once. This made them useful for AI work too. Many AI programs run well on GPUs. GPUs are good at parallel processing. This means they can do the same operation on many pieces of data at the same time. This helps AI training go faster than using CPUs alone. But GPUs are not made only for AI. They need more power and may not be as fast as AI chips for certain tasks.
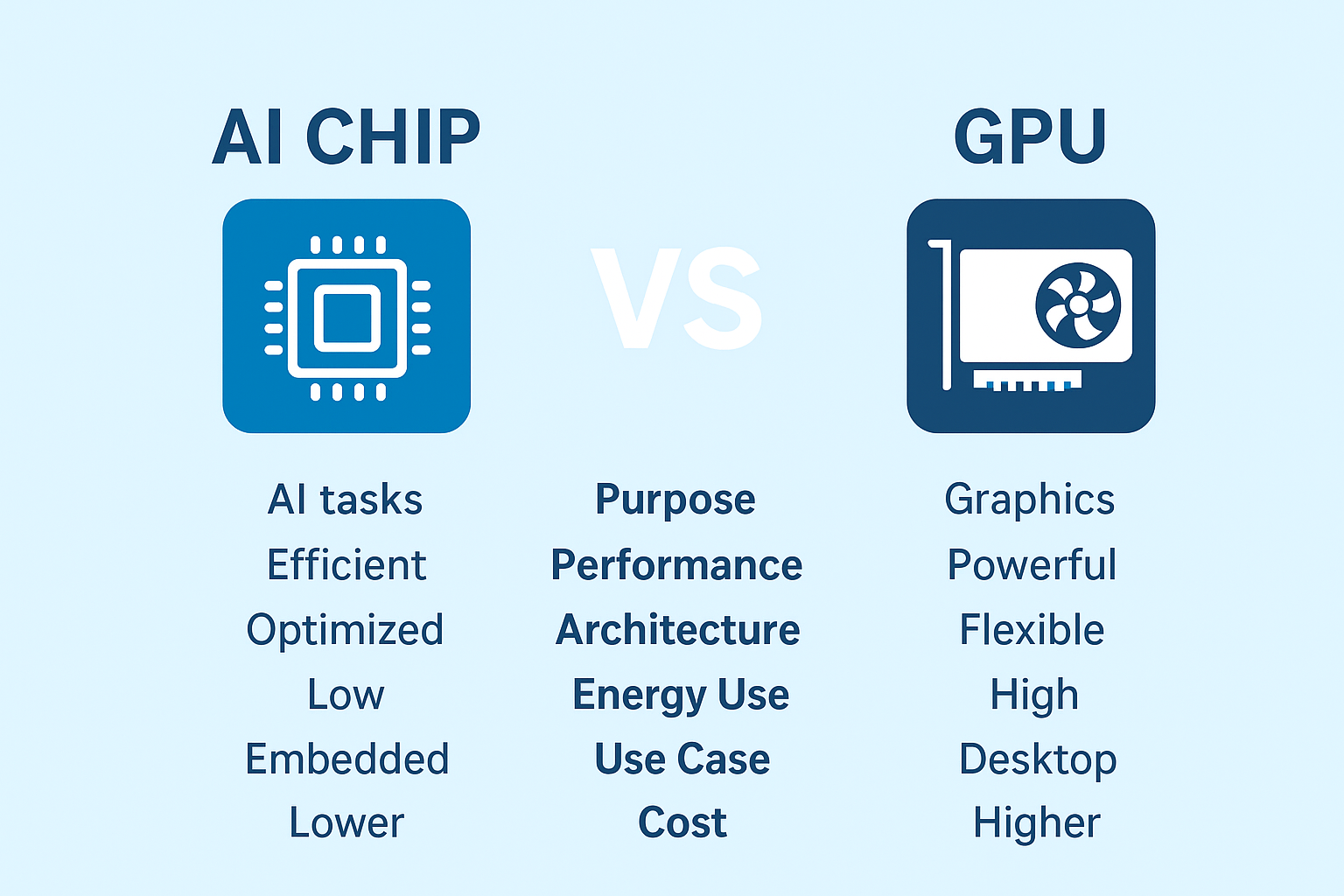
What is the difference between AI and GPU?
The main difference is in the design. AI chips are made with AI in mind. They have special circuits for matrix math and neural networks. GPUs are made for graphics first. AI chips have hardware that moves data in smart ways. This helps with deep learning and machine learning tasks. GPUs move data in ways that are good for images and videos. This is why AI chips can be more efficient for AI programs.
AI chips can also reduce power use. They are built to focus only on AI tasks. GPUs use more electricity because they have more general functions. AI chips can perform the same work while using less energy. This is important for large AI models that need a lot of calculations. Lower energy use also means less heat. This can make machines run more stable over time.
When it comes to speed, AI chips have an advantage. They can process certain AI operations faster than GPUs. For example, tasks like matrix multiplication or tensor operations are faster on AI chips. GPUs are still fast, but they may need more time and power for the same work. This is why big AI companies often use AI chips for training large models. GPUs are still useful for testing and smaller AI programs because they are more common and easier to use.
AI chips also help with scaling. Large AI systems need many calculations. AI chips are made to work together in clusters. This means many chips can handle one big AI program at the same time. GPUs can also work in clusters. But AI chips often need less power and less cooling when doing the same job. This makes them more practical for very big AI projects.
Which one costs more, AI or GPU?
Another point is cost. AI chips can be expensive. They are new and designed for specific AI work. GPUs can be cheaper and easier to buy. Many developers start with GPUs because they are ready to use and have software support. But for very large AI projects, AI chips can save money in power and speed. The cost of electricity and cooling can be high for big AI workloads. AI chips can reduce these costs over time.
AI chips are also designed to support new AI models. These models need special types of math. AI chips can handle these operations efficiently. GPUs can do the work too, but not always as fast. As AI grows, more AI chips are being developed. They are made to meet the needs of modern AI programs. GPUs are still important, but AI chips will play a bigger role in the future.
Both AI chips and GPUs need software support. AI programs need drivers and libraries to use the hardware. AI chips often come with software that is tuned for AI tasks. GPUs have software too, but it is more general. Developers must choose the right hardware and software together. This ensures the program runs fast and uses less energy.
AI chips can come in different types. Some are made for training AI models. Others are made for running AI programs. Training chips focus on speed and power. Inference chips focus on efficiency and low energy use. GPUs can also do both tasks, but they are not optimized for energy. This is why AI chips are chosen for large AI systems where energy use is important.
AI chips are also important in AI at the edge. Edge devices are small computers that run AI programs locally. AI chips in edge devices can do AI work without needing a cloud server. This reduces delay and improves speed. GPUs are often too big and power-hungry for edge devices. This is another reason AI chips are growing in use.
The choice between AI chips and GPUs depends on the work. For big AI projects, training large models, and running many calculations, AI chips are better. For smaller projects, testing, or graphics work, GPUs can be enough. Developers must think about cost, power, speed, and software support. Each option has its strengths.
In the future, AI chips will likely grow in importance. AI programs are getting bigger and need more calculations. AI chips can handle this growth better than GPUs alone. GPUs will still be used because they are flexible and widely available. The combination of AI chips and GPUs can make AI development faster and more efficient. Developers will choose the right tool for each task to get the best results.
In conclusion, AI chips and GPUs are both important. AI chips are made for AI tasks and are fast and efficient. GPUs are made for graphics and parallel processing. AI chips use less power and can handle big AI models better. GPUs are flexible and easier to use. Developers must understand the difference to choose the right hardware. As AI grows, AI chips will become more common. GPUs will still have a role, but AI chips will lead in specialized AI work.